In a latest examine printed on the medRxiv* preprint server, researchers consider the chance of healthcare employees (HCW) turning into contaminated by the extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) following contact with a coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19 )-positive family member. The authors of this examine additionally assessed the chance of healthcare-associated SARS-CoV-2 transmission in a tertiary care mom and baby middle in Canada.
Research: Ought to healthcare employees with SARS-CoV-2 family exposures work? A cohort examine. Picture Credit score: Matteo Benegiamo / Shutterstock.com
Introduction
The SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant grew to become the dominant circulating variant of concern (VOC) within the Quebec (QC) province of Canada by December 20, 2021. Concurrently, there was a rise within the variety of HCWs reporting family exposures of confirmed COVID – 19 circumstances as a result of excessive neighborhood transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant.
The latest provincial COVID-19 tips regard everybody as unprotected and suggest that SARS-CoV-2-infected HCWs isolate for ten days. Moreover, all family contacts ought to quarantine, as research have demonstrated the lack of two-dose COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness in stopping Omicron an infection.
Nonetheless, the tertiary care mom and baby hospital, Middle Hospitalier Universitaire (CHU) Sainte-Justine in QC, Canada, allowed HCWs uncovered to confirmed COVID-19 family circumstances to work if they’ve obtained two or extra doses of COVID-19 vaccines, have been asymptomatic or with signs, obtained a destructive reverse transcription-polymerase chain response (RT-PCR) take a look at, and adopted correct preventive measures as a result of potential threat of workforce shortages.
Concerning the examine
Within the current cohort examine, the researchers decided the chance of HCWs uncovered to a SARS-CoV-2-positive family contact to turn out to be COVID-positive and the chance of nosocomial COVID-19 transmission.
Examine individuals have been HCWs with a historical past of family publicity to SARS-CoV-2-positive circumstances who contacted the CHU Sainte-Justine’s Occupational Well being and Security (OHS) unit, Montreal (QC) Canada, between December 20, 2021, and January 17 , 2022.
The principle end result of the examine was a optimistic RT-PCR take a look at consequence for SARS-CoV-2. A number of information units have been analyzed through the examine, together with HCW vaccination dates and the variety of doses, RT-PCR outcomes and examined dates, signs reported by the HCW through the preliminary take a look at, circumstances of COVID-19 outbreaks amongst HCWs, and healthcare-acquired COVID-19 in sufferers.
The outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 amongst HCWs and nosocomial COVID-19 amongst sufferers have been recognized by the every day analysis of Quebec Ministry of Well being and Social Providers-reported COVID-19 circumstances as a part of the common An infection Prevention and Management surveillance (IPAC) process. Nosocomial SARS-CoV-2 an infection was suspected in sufferers if signs occurred three or extra days after the hospital admission.
Examine findings
Almost 50% of HCWs with a identified SARS-CoV-2-positive family contact remained destructive through the examine interval. Among the many HCWs who grew to become optimistic for SARS-CoV-2, 82.4% examined optimistic through the preliminary RT-PCR take a look at and have been quarantined.
Out of the 279 HCWs allowed to work regardless of having a confirmed COVID-19 family contact, almost 15% grew to become COVID-positive from a median of 4 days after the preliminary SARS-CoV-2 screening take a look at.
The family secondary assault fee (SAR) of Omicron in booster-vaccinated people was 42%. HCWs with out signs or those that obtained booster vaccination greater than seven days earlier than the COVID-positive family publicity had an 88% likelihood of remaining SARS-CoV-2 destructive.
Though a complete of ten COVID-19 outbreaks occurred amongst HCWs through the examine interval, which was outlined as three optimistic HCWs per outbreak, none of those contaminated people was related to an HCW with COVID-positive family contact. Actually, some outbreaks have been related to a family contact after the contact tracing of the COVID-positive HCW.
Among the many 9 sufferers with hospital-acquired COVID-19, six have been related to mother and father of the youngsters, guests, and different COVID-positive sufferers. No supply was recognized for the remaining three circumstances.
Taken collectively, no healthcare-associated SARS-CoV-2 transmission to sufferers or COVID-19 outbreak amongst HCWs was noticed when an HCW with a identified SARS-CoV-2-positive family publicity was allowed to work.
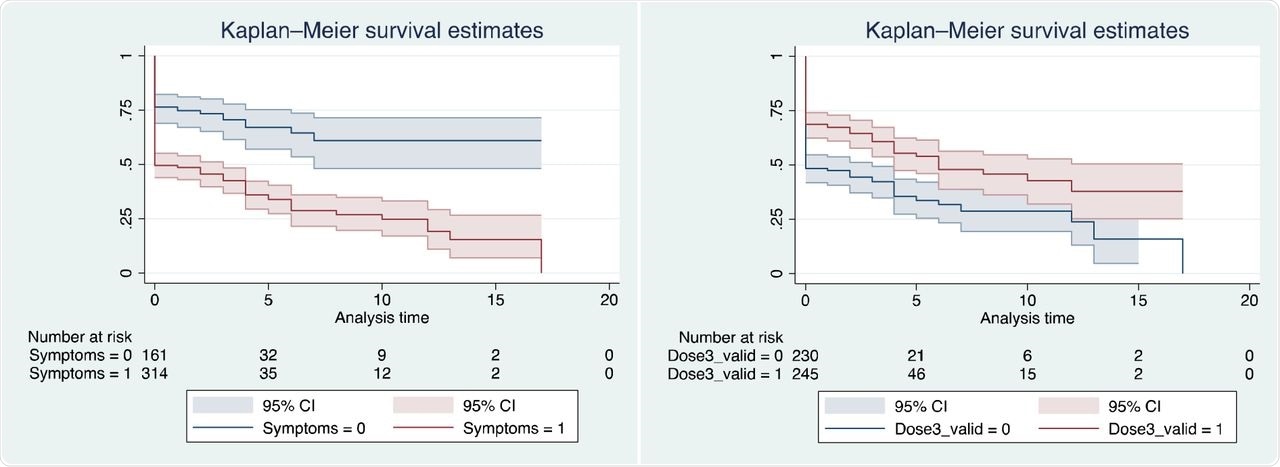
Survival curves for remaining RT-PCR destructive (a) stratified by presence of signs at first take a look at; (b) stratified by vaccination standing.
conclusions
The current examine discovered a 50% family SAR of Omicron, which was larger than these reported in a earlier Danish examine. That is possible due to the excellent end result evaluation within the current examine utilizing the RT-PCR take a look at for diagnosing secondary circumstances, relatively than the rapid-antigen take a look at used within the Danish examine.
The authors counsel that measures carried out to cut back nosocomial COVID-19 must be meticulously balanced with the chance of HCW scarcity in hospitals. Moreover, the correct utilization of non-public protecting tools can effectively restrict SARS-CoV-2 transmission.
Altogether, a number of elements should be thought-about whereas figuring out the importance of quarantining HCWs with a family publicity of confirmed COVID-19 case. These embrace the chance of SARS-CoV-2 transmission to HCWs who’ve a decrease threat of problems, given the upper vaccination charges, the possible impression of SARS-CoV-2 transmission to sufferers in a mother-child care hospital setting, who’ve a greater likelihood of restoration even when contaminated, and the chance to sufferers if extremely specialised employees shortages happen.
General, the examine findings show that contemplating the implications of staffing shortages, permitting booster-vaccinated HCWs with out SARS-CoV-2 signs to work is a secure various through the COVID-19 pandemic.
*Essential discover
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific stories that aren’t peer-reviewed and, due to this fact, shouldn’t be thought to be conclusive, information scientific observe/health-related conduct, or handled as established info.

