Microbiomes have taken on main significance as producers and modulators of the host metabolism and homeostatic equipment. In a brand new research, researchers on the College of Calgary, Canada, explored the metabolomes of mice uncovered to various kinds of microbes to grasp the results and the attainable influences of age and intercourse on these outcomes.
Examine: Microbiota ages the metabolome in an age- and sex-dependent method in mice. Picture Credit score: Volodimir Zozulinskyi / Shutterstock
Introduction
The intestine handles all ingested meals for additional digestion and assimilation. As well as, it harbors a wealth of microbes that produce metabolic byproducts with a number of results on host physiology. Subsequently, adjustments within the intestine microbiome’s composition can shift the intestine’s metabolome as nicely.
As an illustration, the human intestine microbiota produces a wide range of nutritional vitamins and ferments undigested carbohydrates and proteins to provide short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), lactate, and bile acids, amongst different molecules, affecting the immune and coagulation methods, in addition to modulating the neuroendocrine community and influencing the gut-brain axis. These metabolic merchandise could trigger alterations within the kind and abundance of metabolites absorbed by way of the epithelial barrier.
The usage of germ-free mouse fashions (GFMM) is a current advance within the research of microbial results on the intestine metabolome. It allows their separation from the results of host metabolites. The present paper, revealed within the journal Nature Communications, made use of gnotobiotic mouse fashions, together with GFMM and particular pathogen-free mice (SPF).
The gnotobiotic mice (OMM12) had been colonized with a particular set of 12 commensals from every of the 5 main phyla discovered within the mouse intestine. These embody Bacteroidota, Bacillota, Pseudomonadota, Actinomycetota and Verrucomicrobiota.
The researchers studied the metabolites within the peritoneal fluid, serum, liver, spleen, and urine, of mice at numerous ages, from just-weaned infants to each female and male adults.
What did the research present?
The findings present that the host metabolome is pushed most notably by physique dimension, modulated by microbiota, age, and intercourse, in that order.
The intestine reveals completely different areas with distinct metabolite signatures, with probably the most vital similarity being between the higher gastrointestinal (GI) and decrease GI tract of GF vs colonized mice, respectively.
The higher GI tract (GIT) had increased concentrations of amino acids from the weight loss plan, resembling tryptophan, leucine, and histidine, which decreased downstream, most likely attributable to absorption. Sugars, fatty acids, and nucleosides had been current extra abundantly within the decrease GIT attributable to microbial breakdown of proteins, carbs, and nucleic acids. This was mirrored within the considerably increased concentrations of those digestion merchandise in GF mice, which lack any microbes.
Probably the most essential think about figuring out the variations within the metabolite concentrations at every website inside the intestine was the microbiota.
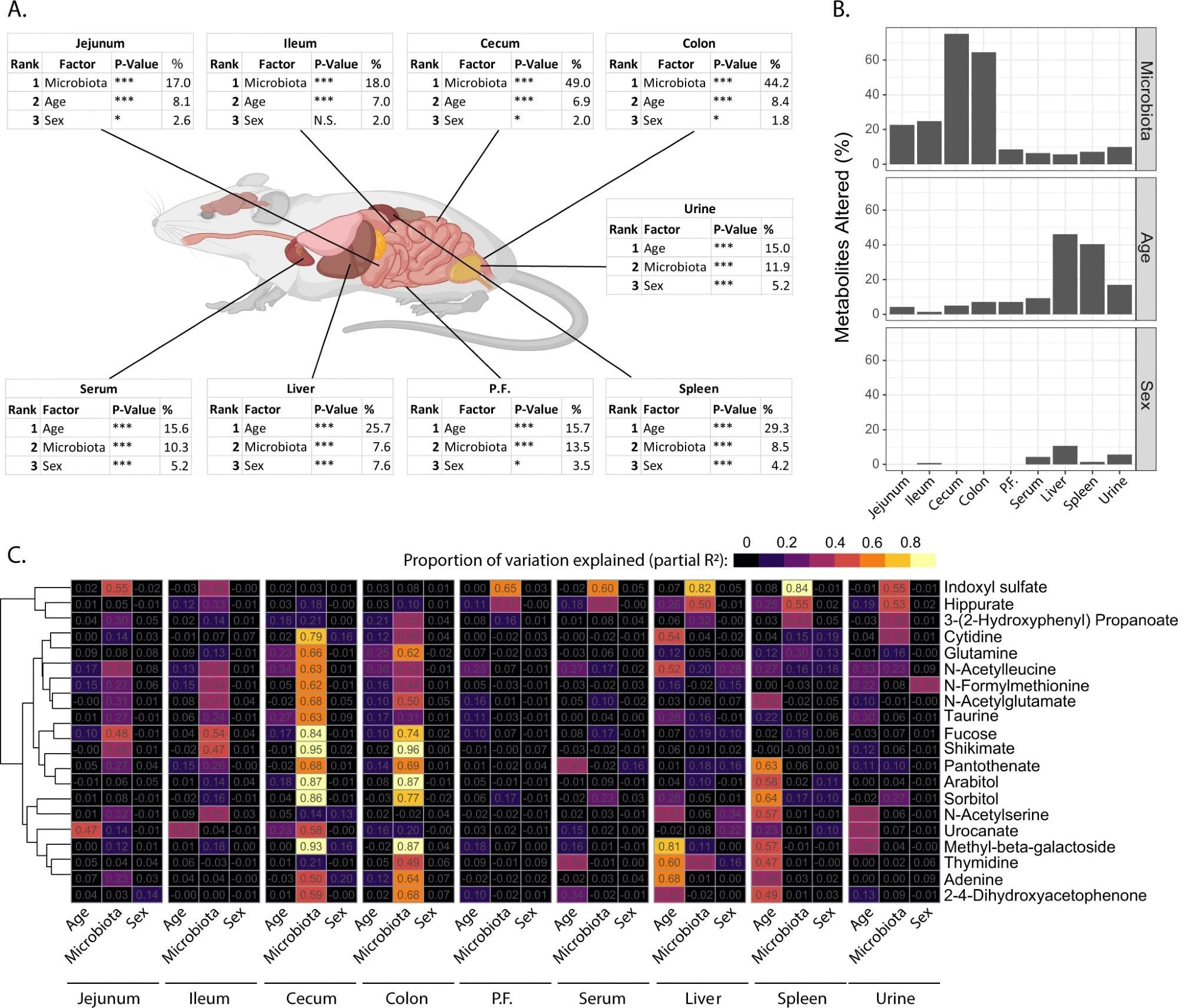 A Estimated proportion of variation defined by microbiota, age and intercourse in every website sampled based mostly on PERMANOVA statistics. B Proportion of metabolites altered (PAdj <0.05) by microbiome, age, and intercourse at every website. C Partial R2 displaying the relative contribution of age, microbiota, and intercourse in explaining the variation in metabolite abundance at every website. Metabolites proven are the 20 metabolites the place probably the most variation was defined by the three elements, full heatmap for all metabolites is proven in Supplementary Determine 1. Information is consultant of n = 72 samples / website (equal illustration from female and male mice, GF, OMM12 and SPF colonized mice and 3-, 8- and 12-week-old mice). PF = peritoneal fluid. Components of Fig. 2A had been generated utilizing Biorender.org underneath license. Supply information are supplied as a Supply Information file.
A Estimated proportion of variation defined by microbiota, age and intercourse in every website sampled based mostly on PERMANOVA statistics. B Proportion of metabolites altered (PAdj <0.05) by microbiome, age, and intercourse at every website. C Partial R2 displaying the relative contribution of age, microbiota, and intercourse in explaining the variation in metabolite abundance at every website. Metabolites proven are the 20 metabolites the place probably the most variation was defined by the three elements, full heatmap for all metabolites is proven in Supplementary Determine 1. Information is consultant of n = 72 samples / website (equal illustration from female and male mice, GF, OMM12 and SPF colonized mice and 3-, 8- and 12-week-old mice). PF = peritoneal fluid. Components of Fig. 2A had been generated utilizing Biorender.org underneath license. Supply information are supplied as a Supply Information file.
Nevertheless, the impact of age was akin to that of microbiota within the variation of metabolites in serum, urine, and peritoneal fluid. Age performed a extra distinguished position in modulating the metabolite profile within the liver and spleen. Intercourse variations brought about probably the most minor impact.
The metabolome within the three mouse fashions additionally confirmed the affect of microbial density and complexity. Within the decrease GIT, the best impact was because of the density of the microbiota, with the OMM12 displaying adjustments in roughly half the metabolites. In distinction, the SPF mice confirmed adjustments in over 60% of metabolites within the colon and over half within the cecum.
Bacterial density is highest in these areas, accounting for the numerous contributions of the microbiota to the host’s metabolism. Nonetheless, the entire GIT confirmed a marked impact on microbial metabolism.
Completely different microbiota composition was mirrored in various metabolite profile. Within the higher GIT, SPF and OMM12 mice had increased cholate ranges in comparison with GF mice, however solely SPF mice had increased taurocholate ranges. Equally, microbes within the SPF mice used up allantoin and raffinose within the decrease intestine, producing glutamine, nicotinate, and guanine, however OMM12 microbes used up solely raffinose and produced solely nicotinate.
Raffinose consists of glucose, fructose, and galactose. The enzyme required for its breakdown, α-galactosidase, is present in microbes however not people or mice. Nicotinate is a crucial micronutrient required for the power cycle of the cell and is derived from the amino acid tryptophan by microbes, other than its availability as such within the weight loss plan.
“The talents of the SPF and OMM12 microbiotas to equally have an effect on the abundance of molecules resembling raffinose and nicotinate means that these could also be nicely conserved metabolic pathways in micro organism, or {that a} particular member of the OMM12 consortia is ready to normalize to the degrees of SPF mice.”
Nevertheless, not one of the 12 commensals in OMM12 mice seem to provide tryptophanase.
Related adjustments had been seen at different non-GI websites as nicely, indicating the “metabolic preferences of microbial communities, which has an impression on metabolite focus.”
The consequences of age on microbial-induced metabolite profiles had been additionally observable, though this was additionally modulated by the native microbiome. GF mice confirmed excessive ranges of uridine and histidine, amongst others, within the decrease GIT at eight weeks in comparison with three weeks. This was not the case when evaluating mice with completely different microbiota, specifically, SPF and GF mice.
This means that the impact of the microbiota on host metabolism varies with the stage of improvement. Some metabolites additionally confirmed vital variation with intercourse in OMM12 or SPF mice however not GF mice, displaying the metabolic variations affected by intercourse hormones in grownup mice mediated by the microbiome.
The research helps to grasp extra about how microbes within the intestine work together with the host by way of metabolites and will help future analysis. As an illustration, it reveals the numerous impact of the particular GI website on the metabolome, outlined mainly by the microbiota.
The absence of a number of metabolic pathways in GF mice underlines the appreciable contribution of the microbiome to human metabolism.
What are the implications?
“Leveraging microbe-metabolite-host interactions in direction of customized drugs holds nice promise for enhancing well being and stopping illness.”
The research reveals that microbes differentially alter the degrees of particular metabolites relying on the presence of sure taxa. As well as, age and intercourse modulated the results of the microbiome on metabolism.
Whereas the research was capable of determine variations in 140 metabolites utilizing semi-targeted strategies, that is solely the tip of the iceberg. A number of orders of magnitude of metabolites stay that haven’t been recognized by these strategies. The research could thus present a sample for future microbiome research regarding these modulators.

