Scientists from the US have carried out a scientific assessment to grasp whether or not cattle enhance the danger of contracting vector-borne illnesses by people. The assessment is at present accessible on the medRxiv* preprint server.
Research: Results of cattle on vector-borne illness danger to people: A scientific assessment. Picture Credit score: smereka/Shutterstock
Background
Hematophagous arthropods, together with mosquitoes, flies, and ticks, are invertebrates that acquire blood as a meals supply from vertebrates in varied methods. Because of this, they will transmit infectious pathogens to people and livestock, main to numerous vector-borne illnesses. Some frequent examples of vector-borne illnesses embody malaria, Lyme illness, Rift valley fever, Chikungunya, West Nile virus, and different bacterial, protozoal, and viral illnesses.
The danger of publicity to vector-borne illnesses is relatively increased for individuals who deal with cattle and livestock at their workplaces, comparable to farmers, agricultural laborers, and slaughterhouse employees.
Within the present systematic assessment, scientists have explored whether or not cattle enhance or lower the danger of human publicity to vector-borne illnesses.
They screened 470 scientific literature revealed in peer-reviewed journals between 1999 and 2019 and chosen 127 research for closing assessments.
The vast majority of chosen research had been carried out in international locations situated in sub-Saharan Africa and southern Asia. The scientists divided these research into three classes, ie, useful, dangerous, or impartial results of cattle on human publicity to vector-borne illnesses.
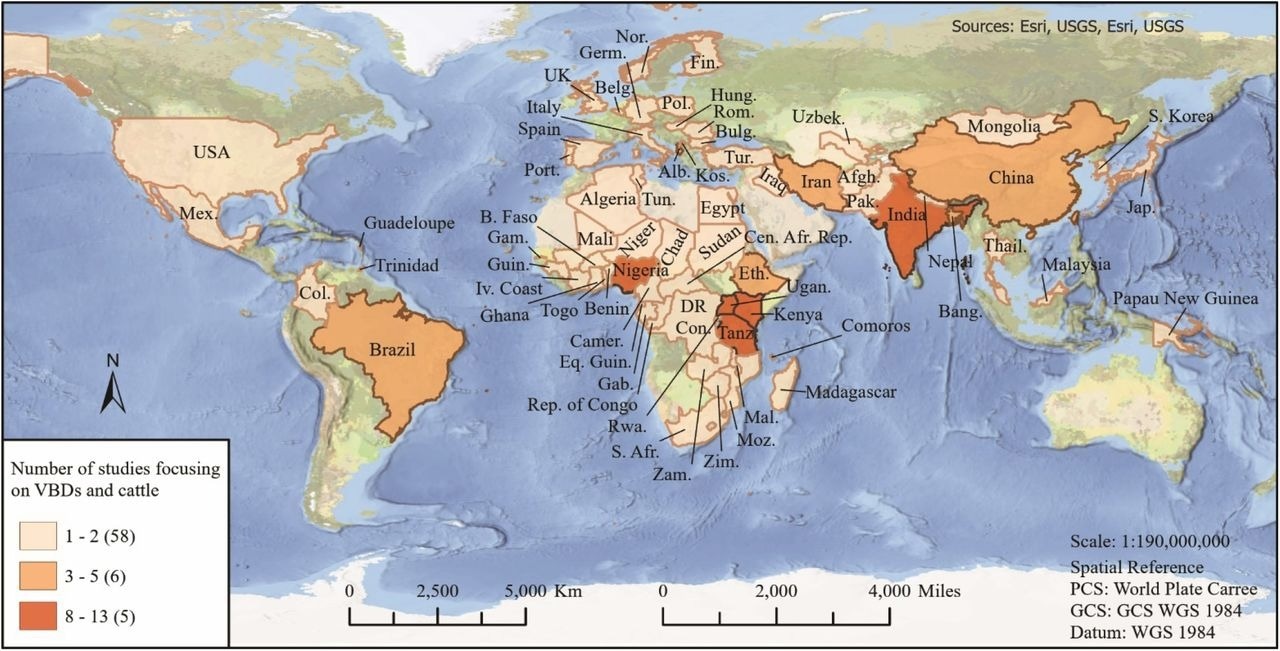
World map representing international locations and variety of research included on this assessment.
Vital observations
The evaluation of chosen research indicated that cattle might both enhance or lower the danger of human publicity to vector-borne illnesses relying on the kind of vector, ecology of pathogens, and livestock administration practices. Furthermore, the evaluation revealed that cattle-mediated danger of publicity is highest for infections transmitted by tsetse flies and ticks, adopted by sandflies and mosquitoes.
A complete of seven mechanisms had been recognized within the assessment by which cattle can influence the danger of human publicity to vector-borne illnesses.
Diversion and attraction of vector blood meals
Cattle can have protecting results in opposition to vector-borne illnesses and may act instead host when disease-carrying vectors favor to feed on cattle as an alternative of people. This useful impact from cattle is known as the zoo-prophylactic impact. Amongst research chosen on this assessment, 16 reported this mechanism.
In distinction, cattle can entice vector bites to people, thereby growing the danger of human publicity to vector-borne illnesses. This impact is known as zoo-potentiation. Amongst research chosen on this assessment, 18 reported this mechanism.
Surroundings
Cattle can modify the atmosphere to make it both appropriate or unsuitable for particular vectors to outlive. By way of this mechanism, cattle can influence the danger of human publicity to vector-borne illnesses.
As cattle grace, they will modify vegetation, which makes the atmosphere unfavorable for some vectors. As well as, cattle sheds modify the soil to a extra alkaline pH. Whereas some vectors favor alkaline soil for mating, some favor soil with impartial pH.
This mechanism was present in six chosen research, indicating that cattle could have protecting or dangerous results relying on the ecological attributes of vectors.
Incompetent host
Cattle can act as an incompetent reservoir host for particular pathogens, such because the Japanese encephalitis virus. These pathogens can not survive longer inside cattle our bodies; thus, the presence of cattle gives a protecting impact in opposition to such infections.
Amongst chosen research, solely three reported this mechanism.
Competent host
Cattle also can act as a reliable reservoir host for sure pathogens, amplifying their progress and supporting lifecycle. In some instances, particular pathogens (Instance: Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense) can survive inside cattle for a very long time with out being detected. These pathogens may give rise to important outbreaks upon the arrival of favorable circumstances.
This was probably the most generally evaluated mechanism within the assessment, with a complete of 63 chosen research reporting about it.
Direct contact transmission
Consumption of dairy merchandise or meat from contaminated cattle can enhance the danger of an infection transmission to people. The most typical examples embody Crimean Congo hemorrhagic fever, tick-borne encephalitis, Rift Valley fever, and Alkhurma/Alkhumra hemorrhagic fever.
Direct contact with dwell or useless contaminated cattle whereas dealing with them in workplaces also can enhance the danger of human publicity to vector-borne illnesses.
This was the second mostly noticed mechanism, with a complete of 28 research reporting about it.
Interplay between cattle and different animals
The motion of cattle from a disease-endemic area to non-endemic areas and interactions between cattle and different animals throughout grazing exercise can result in the transmission of vector-borne illnesses to new geographical areas. Some frequent examples embody babesiosis and trypanosomiasis.
This mechanism was noticed in 26 research included within the assessment.
Insecticidal/acaricidal remedy of cattle
Treating cattle with pesticides/acaricides can considerably cut back the proportion of particular vectors (tsetse flies and mosquitoes) within the atmosphere. This can be a important useful impact of cattle in opposition to vector-borne illnesses.
This mechanism was noticed in 17 research included within the assessment.
General, the assessment demonstrates that cattle can have useful or dangerous results on the danger of human publicity to numerous vector-borne illnesses. Nonetheless, the impact of cattle depends upon sure components, together with the kind of vector, the character of pathogen–atmosphere interplay, and livestock administration practices.
*Vital discover
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific studies that aren’t peer-reviewed and, due to this fact, shouldn’t be thought to be conclusive, information scientific apply/health-related habits, or handled as established data.

