In a latest examine posted to the preprint* server Analysis Sq. whereas beneath assessment for publication in BMC Medical Genomics, researchers examine the potential causal relationship between gastroesophageal reflux illness (GERD) and the chance of heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) throughout common menstrual cycles.
Examine: A causal affiliation between gastroesophageal reflux illness and danger of heavy menstrual bleeding with common cycle: A Mendelian randomization examine. Image Credit score: Africa Studio / Shutterstock.com

 *Vital discover: Analysis Sq. publishes preliminary scientific studies that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be considered conclusive, information medical follow/health-related conduct, or handled as established data.
*Vital discover: Analysis Sq. publishes preliminary scientific studies that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be considered conclusive, information medical follow/health-related conduct, or handled as established data.
What’s GERD?
GERD is a widespread gastrointestinal subject characterised by chest burning and is usually recognized via symptom analysis and endoscopy. The chronicity of GERD is attributed to genetics, physique mass index (BMI), smoking, and probably feminine hormones.
HMB, which impacts two to 5 out of each 10 ladies, considerably diminishes well-being and is linked to signs like nausea. The first causes of HMB vary from uterine issues and systemic issues to sure medicines.
Notably, the connection between GERD and regular-cycle HMB stays underexplored, with some research suggesting a possible position of estrogen in GERD signs.
Concerning the examine
The genome-wide affiliation examine (GWAS) database was utilized for acquiring information from quite a few GWAS, from which abstract statistics for GERD and HMB, each of European descent populations, have been obtained. Particular statistical standards have been used to isolate single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) related to GERD, which led to the identification of 75 SNPs. These SNPs underwent additional evaluation to gauge their relevance to GERD and HMB.
Mendelian randomization (MR) was used to find out the correlation of every SNP to GERD and the affiliation between these SNPs and the chance of HMB in common menstrual cycles. MR evaluation was additionally used to establish the causal relationship between GERD and HMB.
The inverse-variance weighted (IVW) methodology, MR-Egger regression, and weighted median estimator have been used to offer statistical evaluation discerning the causality between GERD and menstrual cycles.
Examine findings
A complete of 75 SNPs have been recognized from GWASs on GERD to be used as instrumental variables (IVs), with 4 SNPs excluded throughout information evaluation. These SNPs had a constructive affiliation with HMB in common menstrual cycles, which was supported by particular P-value and F-statistic standards.
By way of the IVW methodology, proof supporting a causal hyperlink between GERD and HMB throughout common cycles was noticed. Nevertheless, the MR-Egger methodology, which was utilized to examine potential directional pleiotropy, didn’t point out a causal hyperlink. Conversely, the weighted median methodology suggests there is perhaps a causal relationship; nonetheless, the outcomes have been inconclusive.
Upon evaluating the strategies, the IVW methodology exhibited larger precision. Given the constant course throughout all fashions, the Mendelian randomization evaluation suggests a possible causal hyperlink between GERD and HMB throughout common menstrual cycles.
There was no vital proof of horizontal pleiotropy; nonetheless, potential indicators of heterogeneity have been recognized. Notably, no single SNP dominated the IVW estimate. Even when contemplating potential biases in MR strategies as a consequence of horizontal pleiotropy, each the funnel plot and MR-Egger regression confirmed constant outcomes, thus implying no evident asymmetry.
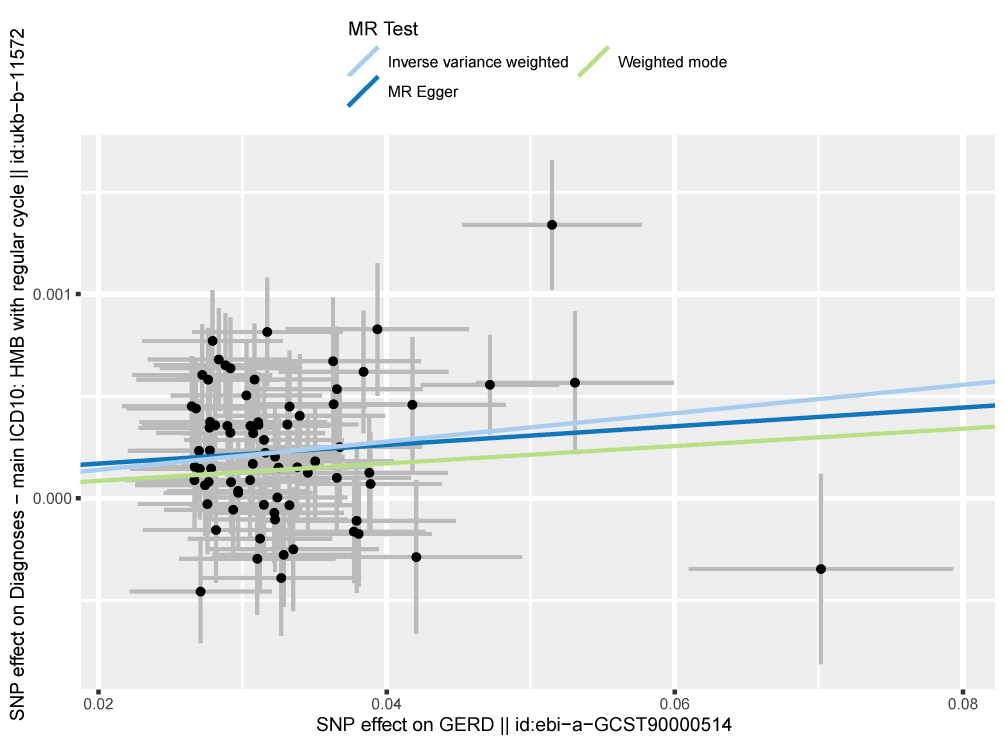
Scatter plots of genetic associations with GERD in opposition to the genetic associations with HMB with regular menstrual cycles. The slopes of every line signify the causal affiliation for every methodology. The blue line represents the inverse‐variance weighted estimate, the inexperienced line represents the weighted median estimate, and the darkish blue line represents the Mendelian randomization‐Egger estimate.
Conclusions
GERD is a fancy dysfunction encompassing numerous syndromes intensified by gastroesophageal reflux. Given its widespread and chronic nature, GERD imposes a major financial pressure, from physician visits to most cancers monitoring.
A earlier Swedish examine highlighted a relationship between physique weight and GERD signs, thus suggesting the potential position of estrogen in GERD. Whereas some ladies report nausea throughout menstruation, different research have reported that elevated intercourse hormones throughout being pregnant contribute to reflux. As a result of confounding variables, conventional epidemiological research face challenges in defining the causality between publicity elements and illness outcomes.
Research have observed a connection between estrogen and GERD. Girls usually show extra GERD signs, whereas males expertise extreme issues. Such gender discrepancies is perhaps estrogen-related.
GERD additionally hyperlinks with hormone alternative remedy and being pregnant, probably indicating an affiliation between estrogen ranges and heavy menstruation.

 *Vital discover: Analysis Sq. publishes preliminary scientific studies that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be considered conclusive, information medical follow/health-related conduct, or handled as established data.
*Vital discover: Analysis Sq. publishes preliminary scientific studies that aren’t peer-reviewed and, subsequently, shouldn’t be considered conclusive, information medical follow/health-related conduct, or handled as established data.
Journal reference:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Ren, X., Wang, Y., Chen, H., et al. (2023). A causal affiliation between gastroesophageal reflux illness and danger of heavy menstrual bleeding with common cycle: A Mendelian randomization examine. Analysis Sq.. doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-3184160/v1

