In a current research printed within the journal Nature Drugs, researchers assessed the coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) vaccine effectiveness (VE) towards symptomatic infections with extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants of concern (VOCs) and variants of curiosity (VOIs) by genetic mismatch/distance (GD) evaluation.
Vaccination is important to curtail transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and for mitigating COVID-19 severity. So far, a handful of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are both within the early use part or have acquired approval for administration to the overall inhabitants. Nevertheless, the safety conferred by vaccines is challenged by the emergence of novel genetic variants.
Examine: Speedy analysis of COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness towards symptomatic an infection with SARS-CoV-2 variants by evaluation of genetic distance. Picture Credit score: Foxeel/Shutterstock
Concerning the research
Within the current research, researchers carried out GD evaluation to guage the VE of COVID-19 vaccines towards symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections based mostly on knowledge from population-based epidemiological research.
The 4 vaccine platforms evaluated had been the messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA)-based vaccines, protein subunit vaccines, viral vector-based vaccines, and inactivated vaccines, which had been acquired by 39, 5, 24, and 10 people, respectively. GDs had been calculated based mostly on the imply hamming distances on the receptor-binding domains (RBDs) of SARS-CoV-2 variants to the strains current within the vaccines.
VE was estimated by mixed-effects modeling by which GD was the important thing predictor and the confounders reminiscent of age and the time elapsed put up the second vaccinations had been managed. VE and GD of the licensed vaccines had been in contrast, and subsequently, the group explored the affect of GD on immune safety suggested by vaccines. The VE values had been estimated towards SARS-CoV-2 VOCs reminiscent of Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron (together with the BA.1 subvariant, the BA.1.1 subvariant, the BA.2 subvariant, and the BA.3 subvariant ), and VOIs reminiscent of Lambda and Mu.
Additional, the VE-GD mannequin was assessed by validation knowledge. VE knowledge from 57 research and 23 research (variant-specific VE) had been used for mannequin coaching and validation, respectively. Additional, SARS-CoV-2 variants had been predicted with their noticed VE not identified. The appliance of the estimated VE by the VE-GD mannequin was assessed in real-time towards the circulating SARS-CoV-2 variant in a particular geographical space, eg, California.
Lastly, the group explored if region-wise vaccines could possibly be developed and if they’d match with the circulating SARS-CoV-2 pressure profiles, for which strains from 13 areas viz. the UK (UK), South Africa, Germany, India, Russia, Malaysia, Hong Kong, California, Japan, New York, Peru, Brazil, and Mexico had been analyzed.
outcomes
Among the many vaccines assessed, VE estimates for the mRNA-based vaccines, protein subunit vaccines, viral vector-based vaccines, and inactivated vaccines had been 90%, 83%, 69%, and 60%, respectively. Of curiosity, the GD of the vaccines exhibited an reverse development, ie, the least GD was noticed for the mRNA-based vaccines, whereas the opposite three vaccines exhibited bigger GD, and these variations could possibly be as a result of various intervals of vaccine analysis. The mRNA-based vaccine trials had been accomplished first throughout the interval when the SARS-CoV-2 inhabitants had comparatively increased homogeneity.
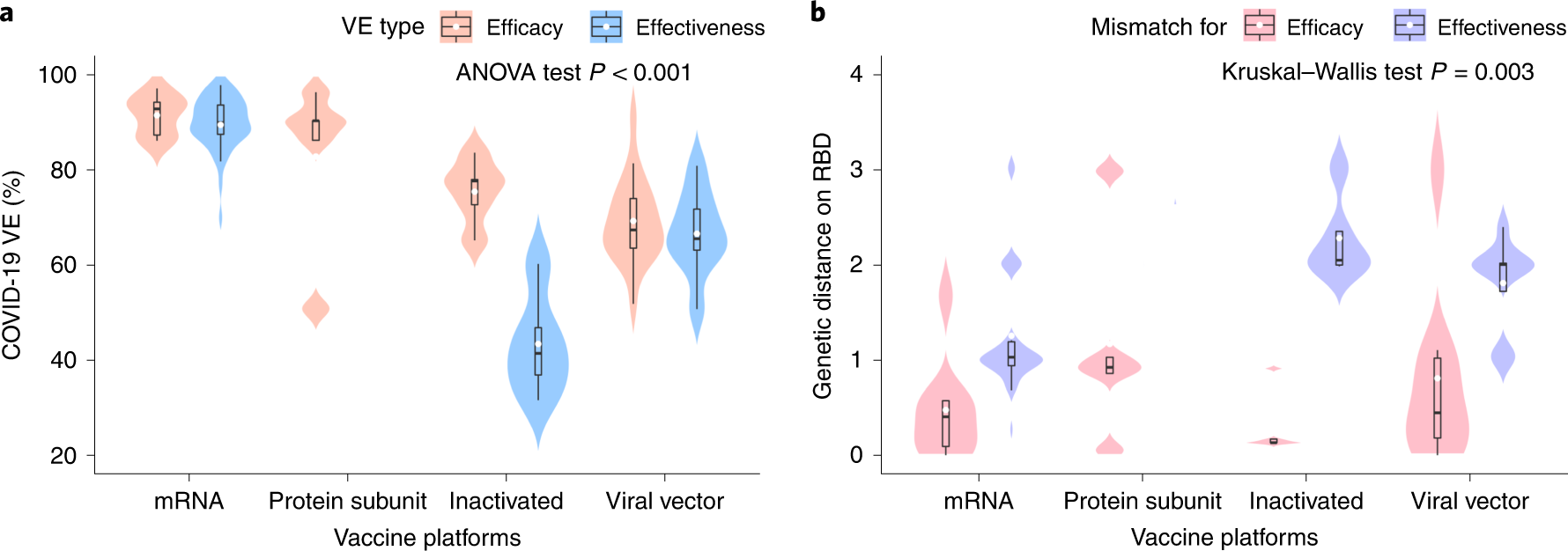 a, Distribution of the VE estimates for various platforms. The VE of mRNA and protein subunit vaccines are increased than different vaccines (two-sided ANOVA check P = 2.2 × 10−14, n = 78). b, Distribution of genetic mismatch on RBD for various vaccine applied sciences. Genetic mismatch is the bottom for mRNA vaccines (two-sided Kruskal–Partitions check P=0.003, n=78). Within the field plots, the center bar signifies the median; the white dot signifies the imply; and the boundaries are Q1 and Q3. Whiskers of the field plot are prolonged to Q3 + 1.5× interquartile vary (IQR) and Q1 − 1.5× IQR.
a, Distribution of the VE estimates for various platforms. The VE of mRNA and protein subunit vaccines are increased than different vaccines (two-sided ANOVA check P = 2.2 × 10−14, n = 78). b, Distribution of genetic mismatch on RBD for various vaccine applied sciences. Genetic mismatch is the bottom for mRNA vaccines (two-sided Kruskal–Partitions check P=0.003, n=78). Within the field plots, the center bar signifies the median; the white dot signifies the imply; and the boundaries are Q1 and Q3. Whiskers of the field plot are prolonged to Q3 + 1.5× interquartile vary (IQR) and Q1 − 1.5× IQR.
Over 86% and 88% of VE variations had been explainable based mostly on their GDs after the random results of the vaccine technological platforms and people of the vaccine merchandise (viz. mRNA-1273, BNT162b2, Ad26.COV2.S, AZD1222, CoronaVac and NVX -CoV2373), respectively had been managed. GD on the S RBD demonstrated probably the most profound affect on the safety conferred by vaccines, whereas no hyperlink was discovered between VE and GD of different SARS-CoV-2 proteins. With every S RBD substitution, VE would lower by 5.2%, 6.8%, 14.3%, and 15.8% for the mRNA-based vaccines, viral vector-based vaccines, protein subunit vaccines, and inactivated vaccines, respectively.
The S protein and N-terminal area (NTD) demonstrated weaker associations between VE and amino acid substitutions. In no GD was current, the VE (by the RBD space) for mRNA-based vaccines and protein subunit vaccines was estimated to be ~96%, whereas the VE for the viral vector-based vaccines and inactivated vaccines had been estimated to be lesser by 20.6% and 17.3%, respectively.
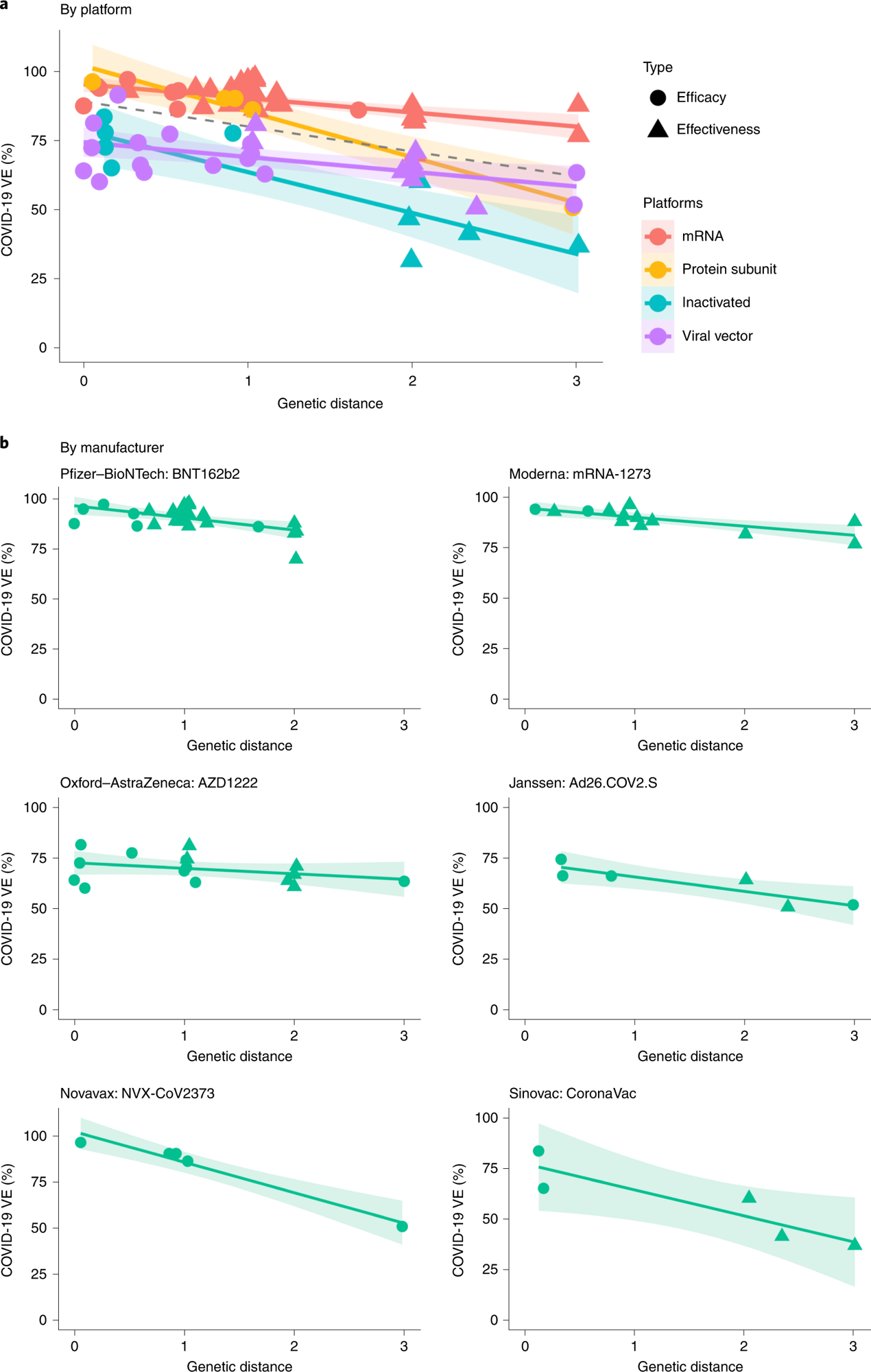
a, Unfavourable linear relationships between VE and GD for various vaccine platforms (P = 0.038, R2 = 86.3%). The dashed line was fitted by all knowledge factors. b, Unfavourable linear relationship between VE and GD for every vaccine product (P = 0.006, R2 = 87.9%). The 2-sided P worth was obtained from the mixed-effects mannequin. The coloured traces had been fitted by knowledge factors of every platform. The shaded space signifies 95% CI.
Predicted VE estimates of the mRNA-based vaccines and the viral vector-based vaccines for Delta had been 82.8% and 61%, respectively, and the corresponding noticed VE values had been 83% and 67% for the BNT162b2 mRNA-based vaccine and the AZD1222 l vector-based vaccines, respectively. Likewise, predicted VE estimates for the BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 vaccines had been 89.4% towards Alpha and 73.7% towards Beta and Gamma, much like the corresponding noticed VE values of 86% and 77%, respectively.
The anticipated VE for the mRNA-1273 vaccine towards Omicron was 14%, much like the noticed VE of 13.9% in December 2021 in California. The findings had been indicative of the elevated validity of the VE-GD method. Predicted VE estimates for mRNA-based vaccines towards the Omicron subvariants had been between 11.9% (Omicron BA.1) and 33.3% (Omicron BA.2).
The mannequin predicted that VE estimates for VOCs apart from Omicron and VOIs reminiscent of Mu and Lambda can be >50% after three months of double mRNA-based vaccination; nonetheless, the VE estimates for inactivated vaccines towards SARS-CoV-2 infections (symptomatic) had been estimated to lower with the emergence of novel genetic variants of SARS-CoV-2.
The Omicron subvariants could possibly be matched to all areas investigated besides Russia within the interval between January 2022 and February 2022; nonetheless, completely different subvariants had been predominant in several geographical areas. The findings indicated that updating vaccine formulations with just one variant could also be insufficient for matching the viral populations current throughout the globe.
Conclusion
General, the research findings highlighted the hyperlink between genetic mismatch of circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants and reported COVID-19 VE based mostly on the mixing of epidemiological research and GD evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 variants. Moreover, the findings indicated that GD values might considerably clarify VE alterations towards SARS-CoV-2 variants, and VE assessments towards evolving pathogens might assist within the improvement of vaccines.

