A latest examine revealed within the Science journal depicted that mosaic receptor-binding area (RBD) nanoparticles immunize from varied sarbecovirus challenges, together with extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), amongst animal fashions.
This infographic illustrates the brand new vaccine, composed of RBDs from eight completely different viruses. The desk reveals the broad spectrum of SARS-CoV-2 variants and associated coronaviruses that the vaccine induces safety in opposition to. Credit score: Courtesy of Wellcome Leap, Caltech, and Merkin Institute
Background
Within the final 20 years, epidemics or pandemics related to SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, two animal CoVs from the sarbecovirus lineage, have affected the human species. Regardless of the fast improvement of potent vaccines, the CoV illness 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic induced by SARS-CoV-2 has been enduring for greater than two years globally. Certainly, the novel SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern (VOCs), such because the severely mutated Omicron VOCs, have protracted the COVID-19 pandemic.
Moreover, the discovering of various sarbecoviruses in bats, a few of which have interaction the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), the entry receptor for SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, will increase the chance of a brand new CoV pandemic. Due to this fact, the event of therapeutics and vaccines to protect in opposition to each zoonotic sarbecoviruses and SARS-CoV-2 VOCs is urgently wanted.
The examine’s authors beforehand categorized SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing anti-RBD antibodies into 4 major courses (class I, II, III, and IV) based on their epitopes and whether or not they recognized down- or up-RBDs on the spike (S) trimers. The vaccine approaches eliciting class III, class IV, and sophistication I/IV antibodies may immunize from doubtlessly creating zoonotic sarbecoviruses and modern and upcoming SARS-CoV-2 variants.
In regards to the examine
Within the current analysis, the scientists outlined animal immunogenicity and virus problem assessments to research mosaic-8 RBD-nanoparticles, a potential pan-sarbecovirus vaccine whereby RBDs from SARS-CoV-2 and 7 animal sarbecoviruses have been bonded covalently to a 60-mer protein nanoparticle.
The workforce used the SARS-CoV-2 Beta RBD for the problem analyses. They created both mosaic-8b, ie, every nanoparticle displaying the SARS-CoV-2 Beta RBD and 7 different sarbecovirus RBDs bonded to the 60 areas, or homotypic, ie, every nanoparticle showcasing 60 replicas of the SARS-CoV-2 Beta RBD , RBD-mi3 nanoparticles. The researchers leveraged the SpyCatcher-SpyTag platform to covalently bond RBDs to C-terminal SpyTag003 sequences to a 60-mer nanoparticle, ie, SpyCatcher003-mi3, to acquire the 2 sorts of RBD-mi3 nanoparticles.
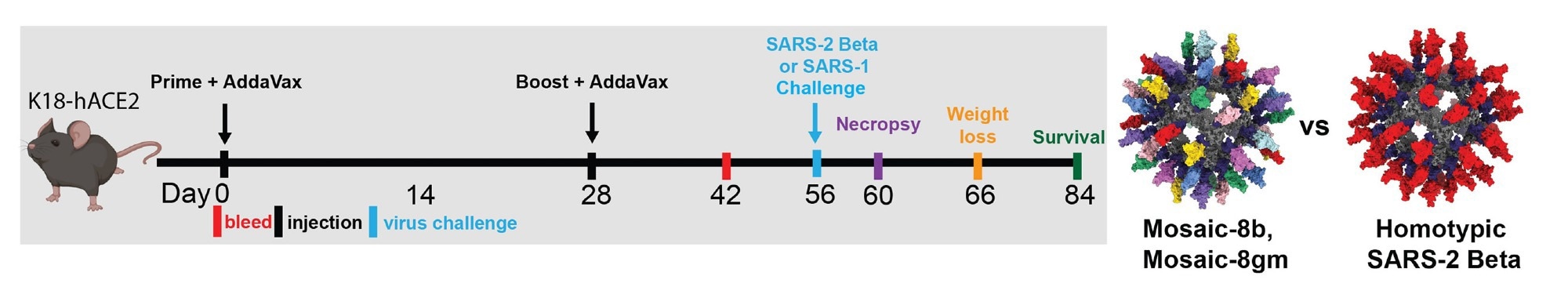 Mosaic-8b and homotypic SARS-2 Beta RBD-mi3 immunizations induced binding and neutralizing antibodies in K18 mice. (A) Left: Immunization schedule. K18-hACE2 mice have been immunized with both 5 μg (RBD equivalents) mosaic-8b, mosaic-8 g, homotypic SARS-2 Beta, or the molar equal of unconjugated SpyCatcher003-mi3 nanoparticles. Proper: Structural fashions of mosaic-8 and homotypic RBD-mi3 nanoparticles constructed utilizing PDB 7SC1 (RBD), PDB 4MLI (SpyCatcher), and PDB 7B3Y (mi3).
Mosaic-8b and homotypic SARS-2 Beta RBD-mi3 immunizations induced binding and neutralizing antibodies in K18 mice. (A) Left: Immunization schedule. K18-hACE2 mice have been immunized with both 5 μg (RBD equivalents) mosaic-8b, mosaic-8 g, homotypic SARS-2 Beta, or the molar equal of unconjugated SpyCatcher003-mi3 nanoparticles. Proper: Structural fashions of mosaic-8 and homotypic RBD-mi3 nanoparticles constructed utilizing PDB 7SC1 (RBD), PDB 4MLI (SpyCatcher), and PDB 7B3Y (mi3).
The authors examined immune reactions and safety from viral an infection in keratin 18-human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (K18-hACE2) transgenic mice to match the effectiveness of homotypic or mosaic RBD-mi3 nanoparticle vaccinations. The 4 cohorts of vaccinated K18-hACE2 mice, every comprising 10 animals, have been contaminated with SARS-CoV-2 Beta or SARS-CoV.
4 days after the problem, the researchers collected lung and oropharyngeal swab samples from 4 teams of K18-hACE2 mice. The scientists assessed the quantities of infectious virus and viral ribonucleic acid (RNA) in these samples.
The workforce additionally carried out homotypic and mosaic RBD-mi3 nanoparticle vaccination and problem exams in non-human primates (NHPs) to develop the present findings to a different animal mannequin of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV an infection. They then investigated if anti-RBD antibodies have been produced in distinct methods by homotypic and mosaic nanoparticles.
outcomes
In line with the examine outcomes, animals vaccinated with homotypic SARS-CoV-2 RBD-mi3 and mosaic-8b RBD-mi3 confirmed safety in opposition to the SARS-CoV-2 problem. The authors famous that mosaic-8b had solely one-eighth as many SARS-CoV-2 RBDs in comparison with its homotypic SARS-CoV-2 equal. These findings suggest {that a} mosaic RBD nanoparticle could also be a COVID-19 vaccination various for stopping current and future SARS-CoV-2 variant infections.
Moreover, mosaic-8b nanoparticles and never homotypic SARS-CoV-2 RBD-mi3 nanoparticles safeguarded K18-hACE2 mice from mortality in response to a mismatched SARS-CoV problem, indicating {that a} mosaic nanoparticle vaccine may also immunize in opposition to sickness introduced on by potential mismatched zoonotic sarbecoviruses.
Though the homotypic nanoparticles didn’t utterly shield from SARS-CoV in K18-hACE2 mice, the authors famous that viral titers in lung tissue acquired from vaccinated animals have been decrease versus the management animals. This inference was related contemplating the potential for mismatched immunity imparted by homotypic SARS-CoV-2 RBD-mi3 nanoparticle vaccination. Since just one out of 4 animals exhibited measurable viral concentrations within the lungs relative to 4 out of 4 within the management cohort, the scientists talked about that some quantity of safety was evident.
The present findings {that a} mosaic RBD safeguarded in opposition to challenges from each mismatched and matched sarbecoviruses, versus homotypic SARS-CoV-2 RBD nanoparticles that absolutely protected solely from a matched problem, have been coherent with RBD mapping investigations exhibiting that antibodies concentrating on conserved RBD territories , not the immunodominant class I and sophistication II RBD epitopes, have been mainly elicited by mosaic-8b but not by homotypic SARS-CoV-2 RBD-mi3 nanoparticles.
conclusions
Collectively, the present work in contrast the immune reactions in macaques and mice evoked by homotypic (simply SARS-CoV-2) and mosaic-8 (SARS-CoV-2 plus seven animal sarbecoviruses) RBD-nanoparticles. The investigators discovered that mosaic-8 provoked vital immune reactions to mismatched viral strains, similar to animal sarbecoviruses and SARS-CoV.
Homotypic SARS-CoV-2 vaccination solely protected against SARS-CoV-2 challenges. Then again, mosaic-8 vaccination demonstrated equal neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants, similar to Omicrons, and immunized in opposition to SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV infections. Following immunization with mosaic-8, epitope mapping revealed heightened addressing of conserved epitopes.
Collectively, the current findings point out that mosaic-8 RBD-nanoparticles might be able to safeguard in opposition to SARS-CoV-2 variants and any future sarbecovirus spillovers.
Journal reference:
- Mosaic RBD nanoparticles shield in opposition to problem by varied sarbecoviruses in animal fashions; Chengcheng Fan, Tiong Okay Tan, Alain R Townsend, Jesse D Bloom, Vincent J Munster, Pamela J Bjorkman, Mark G Lewis, Claudia A Jette, Han Gao, Yu E Lee, Greg Saturday, Anthony West P, Kakutani M Leesa, Priyanthi NP Gnanapragasam, Jonathan E Schulz, Jennifer R Keeffe, Tyler N Starr, Ankur Sharma, Hanne Andersen, Allison J Greaney, Neeltje van Doremalen, Alexander A Cohen. Science, DOI: 10.1126/science.abq0839, https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abq0839

