In a current assessment printed within the journal Rising Infectious Ailments, researchers investigated the literature pertaining to mammalian avian influenza A (H5N1) infections during the last 20 years. Their assessment coated two principal panzootic durations – 2003 to 2019 and the continuing 2020 by means of 2023 – and elucidates the tendencies in H5N1 infections throughout these durations. Their findings counsel that whereas the first supply of viral transmission stays contact with contaminated birds, mammal-to-mammal transmissions are on the rise. These alarming findings spotlight current mutations in H5N1 strains, underscoring the necessity for steady surveillance to mitigate a possible world pandemic.
Synopsis: Current Modifications in Patterns of Mammal An infection with Extremely Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Worldwide. Picture Credit score: Jeremy Richards / Shutterstock
Avian influenza in mammals?
Extremely pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) is a extreme viral illness brought on by subtypes (H5 and H7) of sort A. During the last century, these viruses have triggered repeated endemic waves, spreading quickly and inflicting substantial losses of avian fauna throughout a variety of species, particularly human-reared poultry.
Since 2003, nonetheless, HPAI A (H5N1) has been noticed to breach kingdom obstacles and leap from their avian hosts to mammals, leading to two unpreceded panzootic occasions – 2003 to 2019 and the continuing 2020 by means of 2023 interval. These occasions have triggered alarm bells inside the scientific group as a result of mutant H1N5 strains affecting endangered wildlife, the financial losses related to their infecting livestock, and their potential for human transmission.
Restricted experiences on the continuing panzootic interval counsel that it’s considerably extra extreme than the 2003 one. It’s projected to be one of many worst panzootic occasions in recorded historical past throughout financial, geographic protection, and animal morbidity and mortality scales. Within the three years because the creation of the panzootic, the virus has unfold throughout 4 continents and a report 26 nations, notably infecting minks, foxes, ferrets, seals, and home cats, all of which current the potential for human transmission.
Sadly, analysis on H1N5 and the continuing panzootic stays scarce and restricted to ‘grey literature’ (non-peer-reviewed information and experiences from authorities databases and web sites). Understanding the evolution of the H5N1 virus and the mutations permitting emergent strains to far outdo their ancestral virus in infectivity and species unfold would higher equip policymakers and scientists alike with the knowledge required to attenuate the continuing panzootic earlier than it explodes right into a full-fledged pandemic.
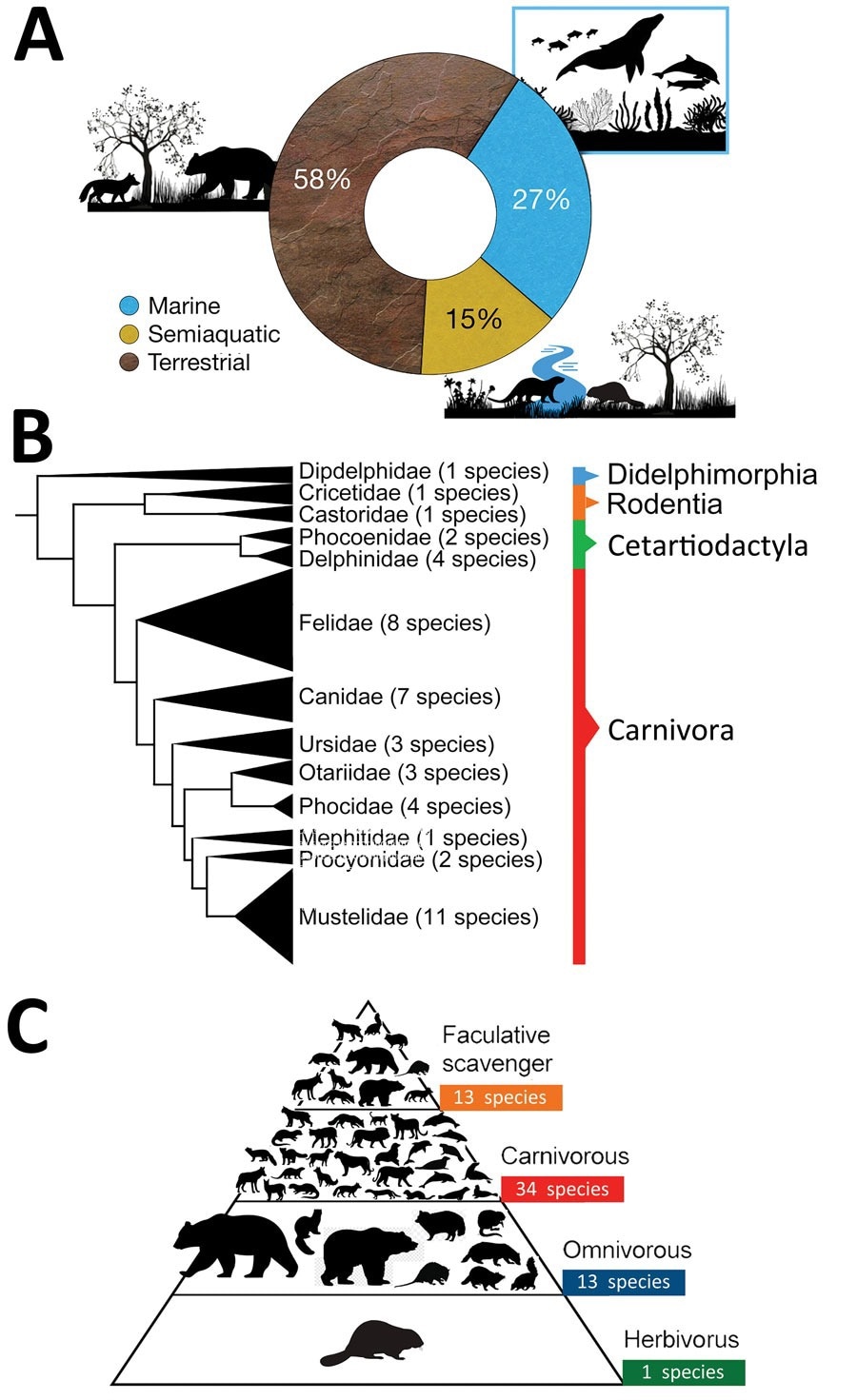
Traits of mammal species affected worldwide by extremely pathogenic influenza virus A (H5N1) the present panzootic (2020–2023). A) Habitat of mammal species affected by H5N1. B) Phylogeny of mammal species affected (tree constructed utilizing iTOL model 5 following Letunic and Bork, from DNA sequence knowledge out there in Upham et al.). C) Trophic stage (facultative scavenger, carnivore, omnivore, or herbivore) of mammal species affected worldwide by H5N1. Among the omnivorous and carnivorous mammals included within the pyramid (n = 13) additionally eat carrion; thus, they’re additionally thought of to be facultative scavengers and are integrated within the higher a part of the pyramid.
Concerning the research
Within the current assessment, researchers compiled and analyzed scientific literature on pure mammalian H5N1 infections (together with people) and in contrast findings from the present panzootic to these from earlier H5N1 waves. The assessment focuses on the quantity and habitats of contaminated species, their phylogeny, an infection sources, and necropsy findings. They additional examine the viral mutations that allow cross-species transmission and elucidate potential dangers to biodiversity and human well being.
Knowledge was collected from the Scopus and Google Scholar on-line databases, with searches divided into two durations – 1996 to 2019 and 2020 to 2023. Research primarily based on serologic proof have been excluded from analyses as a result of uncertainty on the time of an infection, which can bias diagnostic outcomes. Moreover, the World Organisation for Animal Well being, the UK’s Animal and Plant Well being Company, and the USA of America (US) Division of Agriculture’s Animal and Plant Well being Service have been queried for up-to-date info on the present panzootic.
Knowledge from the World Well being Group (WHO) was collated for info on human infections. Lastly, conservation statuses of contaminated species have been derived from the Worldwide Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Crimson Checklist of Threatened Species, their diets and habitats from MammalBase, and H5N1 sequence knowledge from Upham et al. (2019).
Research findings
The database literature assessment revealed 59 publications on mammalian H5N1 infections, 23 of which mentioned earlier H5N1 waves and 36 on the continuing panzootic. Scientific curiosity within the ongoing panzootic is straight away evident – extra mammalian an infection knowledge has been generated within the final three years than was generated within the previous 23.
Alarmingly, whereas earlier waves mixed reported 10 contaminated nations unfold throughout three continents (Asia, Europe, and Africa), the continuing panzootic has already unfold to 26 nations throughout Europe, South America, North America, and Asia. Restricted testing and reporting from different nations means that these findings are underestimations.
“Our assessment means that H5N1 virus is increasing its geographic vary to new continents corresponding to North and South America. This reality is of concern as a result of when an rising pathogen reaches naive populations, the implications for biodiversity may be catastrophic, particularly for threatened species.”
Investigations into the variety of species affected reveal that whereas earlier panzootics cumulatively contaminated 9 predominantly terrestrial and semi-aquatic species, the present panzootic has already been detected in additional than 48 mammalian species, together with 13 species of marine mammals. Peru, Chile, and Argentina have reported hundreds of lifeless people of seals and related mammals (e.g., the American sea lion [Otaria flavescens]), virtually leading to localized extinction occasions.
Prices to biodiversity are vital – to date, avian influenza has affected 4 near-threatened, 4 endangered, three susceptible, and one critically endangered species as in comparison with earlier panzootics, which cumulatively contaminated two endangered and two susceptible species.
Similarities to earlier pandemics do exist – most affected mammals are carnivores (primarily apex- and mesopredators) and scavengers, comparable to the most probably an infection sources – shut contact (together with ingestion) with lifeless or dying birds or contaminated carrion.
…within the yr 2004, a complete of 147 tigers and a couple of leopards housed in zoos in Thailand grew to become contaminated and died after consuming contaminated hen carcasses. Within the present panzootic, the primary case of H5N1infection in minks in Spain was in all probability brought on by contact with contaminated birds (maybe gulls).”
No less than 5 publications have reported an alarming development in viral adaptation – H5N1 strains with novel mutations which will permit for mammal-to-mammal transmission have been recognized. If these strains unfold, fashions counsel {that a} world pandemic might happen quickly, inflicting unprecedented biodiversity and financial loss.
Lastly, H5N1 has been discovered to have spilled over and contaminated at the least 878 people and resulted in 458 deaths (52% lethality) with shut contact with livestock (particularly poultry) deemed the principle transmission route.
“Up to now, no proof signifies human-to-human transmission, and the danger for a pandemic occasion nonetheless appears low. Nevertheless, some of the extreme influenza viruses to have affected people (i.e., Spanish influenza [1918–1919]) developed from an avian influenza virus that tailored to people, a undeniable fact that must be thought of when assessing the spillover threat. Governments should assume accountability for safeguarding biodiversity and human well being from illnesses brought on by human actions. If we hope to preserve biodiversity and defend human well being, we should change the way in which we produce our meals (poultry farming, on this particular case) and the way we work together with and have an effect on wildlife.”
Journal reference:
- Plaza PI, Gamarra-Toledo V, Rodríguez Euguí J, Lambertucci SA. Current adjustments in patterns of mammal an infection with extremely pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus worldwide. Emerg Infect Dis. 2024 Mar, DOI – 10.3201/eid3003.23109, https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/30/3/23-1098_article

