Coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID19) brought on by extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2 or CoV2) and tuberculosis (TB) brought on by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) – are two deadly world respiratory infections with excessive mortality charges. Each these infections pose a big well being problem and financial burden worldwide.
Though concurrent Mtb/CoV2 an infection can exacerbate the signs of TB, the COVID 19 mortality fee amongst people with a earlier Mtb an infection seems to be decrease. This might be on account of a similarity between CoV2 antigens and proteins expressed by the Mycobacterium spp.
Thus, a previous TB an infection will doubtless confer heterologous immunity in opposition to SARS-CoV-2.
Research: Mice contaminated with Mycobacterium tuberculosis are immune to acute illness brought on by secondary an infection with SARS-CoV-2. Picture Credit score: Kateryna Kon
the examine
A latest examine revealed within the journal PLOS Pathogens evaluated the impression of Mtb an infection on secondary CoV2 an infection.
This examine detailed the applying of two COVID-19 mouse fashions (utilizing chronically contaminated Mtb mice) – SARS-CoV-2 an infection of K18-hACE2 mice and mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 an infection of C57BL/6 mice.
outcomes
To check if prior Mtb an infection impacts the response to CoV2 an infection, K18-hACE2 (ACE2) and C57BL/6 (B6) mice had been contaminated with Mtb, and submit thirty days, had been uncovered to CoV2.
Right here, three teams of mice had been monitored – ACE 2 mice with simultaneous Mtb/CoV2 an infection (MtbPOS CoV2POS); sterile media challenged ACE2 mice with prior Mtb an infection (MtbPOS CoV2NEG) – management group; and CoV2 challenged ACE2 mice with out earlier Mtb an infection (MtbNEG CoV2POS – one other management group. The mice had been euthanized and studied 4, 7, and 14 days post-challenge.
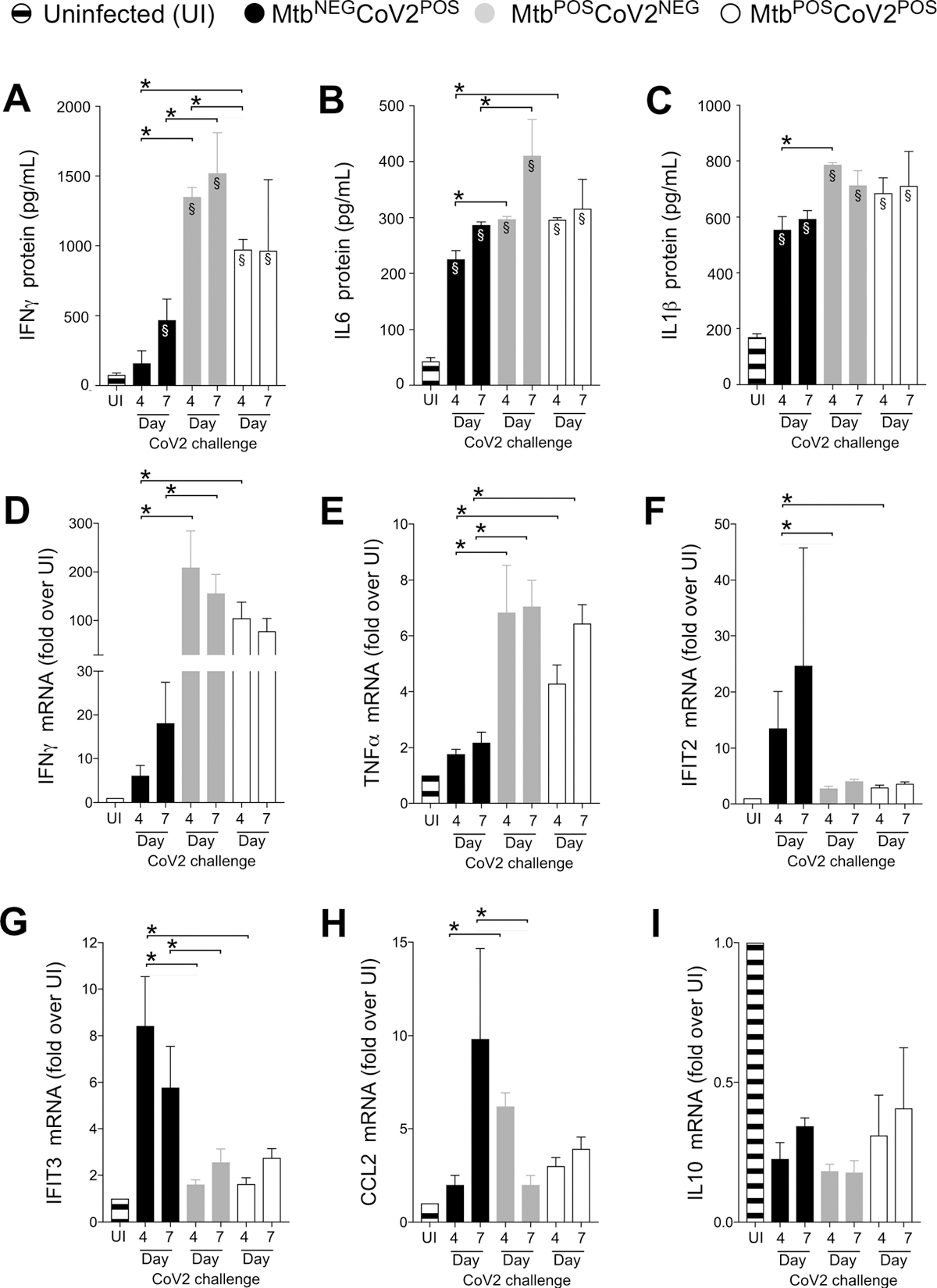
CoV2-elicted cytokine responses are muted within the presence of Mtb an infection. On the indicated days, lung tissue from MtbNEGCoV2POS, MtbPOSCoV2NEG, MtbPOSCoV2POS and uninfected (UI) ACE2 mice was used to measure (AC) protein ranges of (A) IFNγ, (B) IL6 and (C) IL1β, in addition to (TUE) mRNA ranges of (D) IFNγ, (E) TNFα, (f) IFIT2, (G) IFIT3, (H) CCL2 and (I) IL10. This experiment was repeated twice, every with related outcomes (4 mice/group/timepoint). *, p ≤ 0.05 as decided by both Scholar’s t-test or ANOVA; §, vital relative to UI protein ranges.
On day-7, the MtbNEG CoV2POS management misplaced vital weight, whereas weight reduction was insignificant in MtbPOS CoV2POS ACE2 mice—which had been indistinguishable from the MtbPOS CoV2NEG ACE2 mice.
On the 4th day post-challenge, CoV2 burden within the lungs was discovered to be decrease within the MtbPOS CoV2POS group in comparison with the MtbNEG CoV2POS management. The lungs, liver, and spleen of the MtbPOS CoV2POS group and the MtbPOS CoV2NEG management had been related post-challenge – suggesting that they remained unaffected by Mtb progress post-CoV2 an infection.
The variety of acid-fast bacilli (AFB) within the lungs was comparable within the MtbPOS CoV2POS group and the MtbPOS CoV2NEG management. The colony-forming unit (CFU) burden in Mtb-infected B6 controls was similar to the MtbPOS CoV2NEG management indicating an unaffected Mtb progress by the expression of transgenic human ACE2.
An evaluation of CoV2 induced immune response post-Mtb an infection was finished. A number of inflammatory genes had been expressed within the lungs post-CoV2 an infection. On days 4 and seven post-challenge, the degrees of interleukin (IL)1b, IL6, and interferon (IFN)a had been elevated within the MtbNEG CoV2POS lungs in comparison with these within the uninfected controls; the degrees had been even greater for the MtbPOS CoV2NEG management.
In the meantime, MtbPOS CoV2POS resistance couldn’t be related to greater ranges of antiviral genes (IFIT2 and IFIT3), which had been expressed in MtbNEG CoV2POS controls. Concurrent Mtb/CoV2 an infection didn’t induce CCL2 expression.
Of observe, on days 4 and seven post-challenge, MtbNEG CoV2POS controls exhibited alveolar necrosis and diffuse alveolar injury. Terminal bronchiole pneumonia and formation of the hyaline membrane had been famous in MtbNEG CoV2POS controls, which had been absent in MtbPOS CoV2POS lungs. Particular person measurement and the cumulative space occupied by TB granules had been comparable between MtbPOS CoV2POS and MtbPOS CoV2NEG lungs. As well as, immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining optimistic areas had been much less intense among the many MtbPOS CoV2POS lungs in comparison with MtbNEG CoV2POS lungs.
The identical experiments had been carried out with mouse-adapted CoV2 (MACoV2) contaminated B6 mice to evaluate whether or not CoV2 resistance was particularly seen with the ACE2 transgenic mannequin. The examine teams had been – MtbNEG MACoV2POS, MtbPOSMACoV2POS, and MtbPOS MACoV2NEG.
This time, the lack of physique weight within the MtbNEG MACoV2POS mice was much less dramatic. No weight reduction, decrease viral burden, and unchanged Mtb burden in lungs had been detected within the MtbPOSMA CoV2POS mice. Whereas, the MtbNEG MACoV2POS mice exhibited elevated IFIT3, IFITM3, IFNa, ACE2, and IL6. Moreover, IL6 and IFNa had been excessive within the MtbPOS MACoV2NEG group, which remained unaffected post-challenge.
IFIT3 was expressed in each, MtbPOSMA CoV2POS and MtbNEG MACoV2POS teams, and extra so within the latter group. The resistance can’t be attributed to the absence of ACE2 expression within the lungs. Furthermore, the MACoV2 problem didn’t have an effect on MtbPOSMACoV2POS lungs, in contrast to the MtbNEG MACoV2POS group.
Moreover, the MACoV2 resistance-associated immune setting in Mtb contaminated mice lungs had been studied by analyzing dwell lung CD45+ cells in every group, Seventh-day post-challenge. Out of the 12 clusters, two B-cell clusters, 4 T-cell clusters, one basophil cluster, one neutrophil cluster, three myeloid-cell clusters, and one natural-killer (NK) cell cluster had been recognized.
Though the quantity diverse between teams, it was seen that fifty% of the UI lung comprised of an innate cluster—the remainder being T-cells and B-cells. T-cell cluster, B-cell cluster, MPOS cluster, and DC cluster had been greater within the MtbNEG MACoV2POS lungs.
The MtbPOS MACoV2NEG lung revealed relative will increase in all immune clusters on the expense of naïve T-cells, NK cells and neutrophils, in comparison with UI lungs. The resemblance of MtbPOSMACoV2POS, and MtbPOS MACoV2NEG lungs was comparable besides CD8 reminiscence T-cell, DC, expanded B cell, and activated B-cell clusters on the expense of naïve T-cells, NK cells, and neutrophils.
It was inferred that the resistance of MtbPOS MA CoV2POS mice relies upon upon the immune setting of the lungs. Apart from the expanded B- and T-cell clusters, the lung immune setting of the MtbPOSMA CoV2POS mice and Mtb monoinfected lungs had been related.
Subsequently, Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected B6 mice had been discovered to be immune to CoV2 secondary an infection. Mtb an infection results in an irritation that makes the lungs immune to CoV2 propagation and the ensuing immunopathological responses; nevertheless, the entry of CoV2 into cells stays unaffected.
These results might both happen because of the innate immune lineages current within the lungs after Mtb an infection – which limit CoV2; and/or the adaptive immune response elicited by Mtb that confers heterologous immunity by cross-reacting with the CoV2 antigens.
Conclusion
Therefore, it was concluded that prior an infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis protects in opposition to secondary SARS-CoV-2 an infection.